Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Optic Flow
This example shows how to create a Flow to compute optical spectra with optic (independent particle approximation, no local field effects) and perform a convergence study with respect to the k-point sampling.
import sys
import os
import abipy.data as abidata
import abipy.abilab as abilab
import abipy.flowtk as flowtk
def build_flow(options, paral_kgb=0):
"""
Build flow for the calculation of optical properties with optic + band structure
along high-symmetry k-path. DDK are computed with 3 k-meshes of increasing density
to monitor the convergece of the spectra.
"""
# Working directory (default is the name of the script with '.py' removed and "run_" replaced by "flow_")
if not options.workdir:
options.workdir = os.path.basename(sys.argv[0]).replace(".py", "").replace("run_", "flow_")
multi = abilab.MultiDataset(structure=abidata.structure_from_ucell("GaAs"),
pseudos=abidata.pseudos("31ga.pspnc", "33as.pspnc"), ndtset=2)
# Usa same shifts in all tasks.
shiftk = [[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],
[0.5, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.5, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.0, 0.5]]
# Global variables.
multi.set_vars(ecut=2, paral_kgb=paral_kgb)
# Dataset 1 (GS run)
multi[0].set_vars(tolvrs=1e-8, nband=4)
multi[0].set_kmesh(ngkpt=[4, 4, 4], shiftk=shiftk)
# NSCF run on k-path with large number of bands
multi[1].set_vars(iscf=-2, nband=20, tolwfr=1.e-9)
multi[1].set_kpath(ndivsm=10)
# Initialize the flow.
flow = flowtk.Flow(options.workdir, manager=options.manager)
# GS to get the density + NSCF along the path.
scf_inp, nscf_inp = multi.split_datasets()
bands_work = flowtk.BandStructureWork(scf_inp, nscf_inp)
flow.register_work(bands_work)
# Build OpticInput used to compute optical properties.
optic_input = abilab.OpticInput(
broadening=0.002, # Value of the smearing factor, in Hartree
domega=0.0003, # Frequency mesh.
maxomega=0.3,
scissor=0.000, # Scissor shift if needed, in Hartree
tolerance=0.002, # Tolerance on closeness of singularities (in Hartree)
num_lin_comp=2, # Number of components of linear optic tensor to be computed
lin_comp=(11, 33), # Linear coefficients to be computed (x=1, y=2, z=3)
num_nonlin_comp=2, # Number of components of nonlinear optic tensor to be computed
nonlin_comp=(123, 222), # Non-linear coefficients to be computed
)
# ddk_nband is fixed here, in principle it depends on nelect and the frequency range in chi(w).
ddk_nband = 20
# Perform converge study wrt ngkpt (shiftk is constant).
ngkpt_convergence = [[4, 4, 4], [8, 8, 8], [16, 16, 16]]
from abipy.flowtk.dfpt_works import NscfDdksWork
for ddk_ngkpt in ngkpt_convergence:
# Build work for NSCF from DEN produced by the first GS task + 3 DDKs.
# All tasks use more bands and a denser k-mesh defined by ddk_ngkpt.
ddks_work = NscfDdksWork.from_scf_task(bands_work[0], ddk_ngkpt, shiftk, ddk_nband)
flow.register_work(ddks_work)
# Build optic task to compute chi with this value of ddk_ngkpt.
optic_task = flowtk.OpticTask(optic_input, nscf_node=ddks_work.task_with_ks_energies,
ddk_nodes=ddks_work.ddk_tasks, use_ddknc=False)
ddks_work.register_task(optic_task)
return flow
# This block generates the thumbnails in the AbiPy gallery.
# You can safely REMOVE this part if you are using this script for production runs.
if os.getenv("READTHEDOCS", False):
__name__ = None
import tempfile
options = flowtk.build_flow_main_parser().parse_args(["-w", tempfile.mkdtemp()])
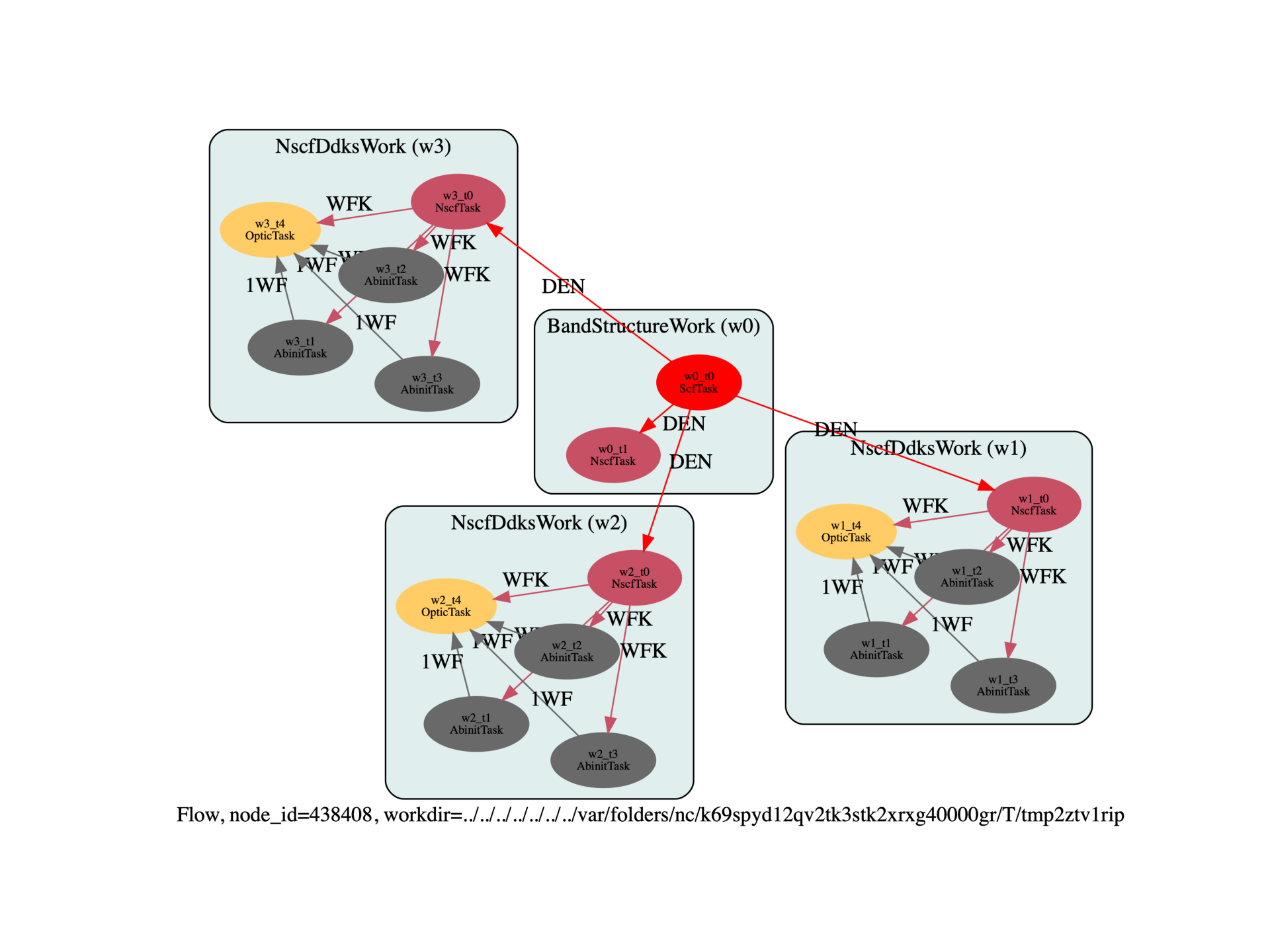
build_flow(options).graphviz_imshow()
@flowtk.flow_main
def main(options):
"""
This is our main function that will be invoked by the script.
flow_main is a decorator implementing the command line interface.
Command line args are stored in `options`.
"""
return build_flow(options)
if __name__ == "__main__":
sys.exit(main())
Run the script with:
run_optic.py -s
then use:
abirun.py flow_optic robot optic
to create a robot for OPTIC.nc files. Then inside the ipytho shell type:
In [1]: %matplotlib
In [2]: robot.plot_linopt_convergence()
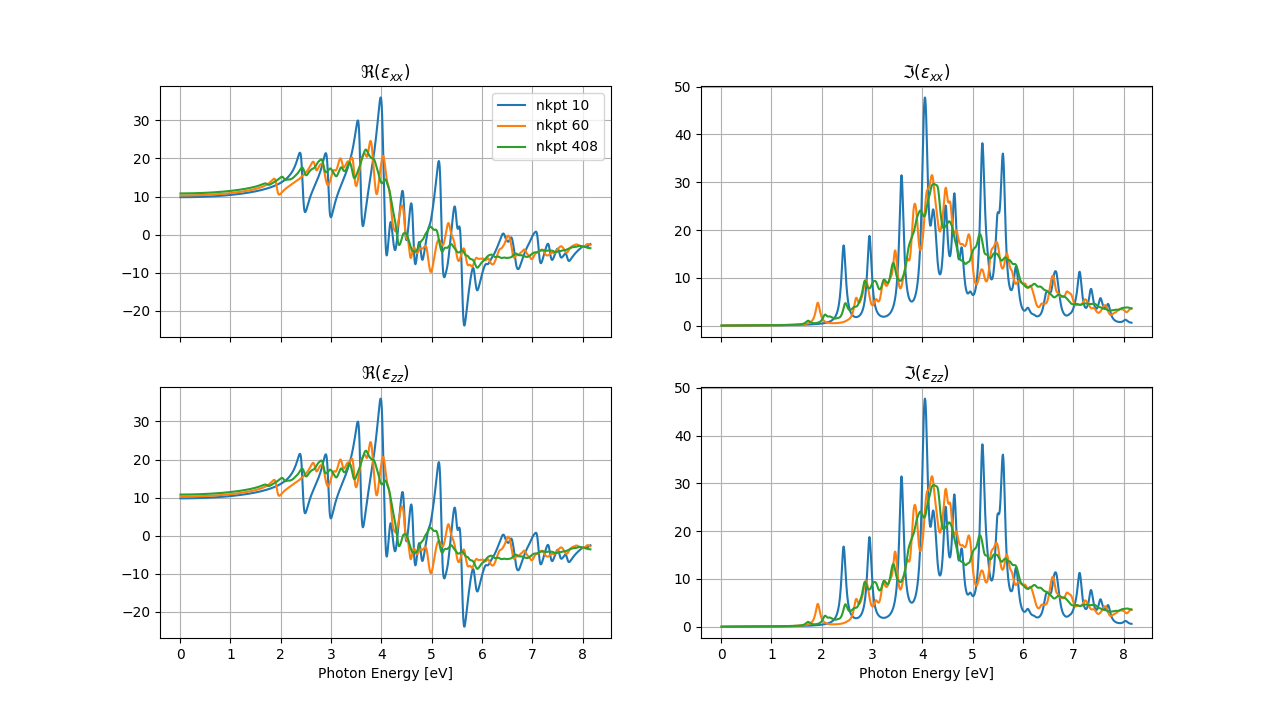
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.927 seconds)