Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Raman with BSE and frozen phonon
This script shows how to perform a Raman calculation with excitonic effects included with the Bethe-Salpeter formalism.
import sys
import os
import numpy as np
import abipy.abilab as abilab
import abipy.data as abidata
from abipy import flowtk
def build_flow(options):
# Working directory (default is the name of the script with '.py' removed and "run_" replaced by "flow_")
if not options.workdir:
options.workdir = os.path.basename(sys.argv[0]).replace(".py", "").replace("run_","flow_")
flow = flowtk.Flow(options.workdir, manager=options.manager)
pseudos = abidata.pseudos("14si.pspnc")
# Get the unperturbed structure.
base_structure = abidata.structure_from_ucell("Si")
etas = [-.001, 0, +.001]
ph_displ = np.reshape(np.zeros(3*len(base_structure)), (-1,3))
ph_displ[0,:] = [+1, 0, 0]
ph_displ[1,:] = [-1, 0, 0]
# Build new structures by displacing atoms according to the phonon displacement
# ph_displ (in cartesian coordinates). The Displacement is normalized so that
# the maximum atomic diplacement is 1 Angstrom and then multiplied by eta.
modifier = abilab.StructureModifier(base_structure)
displaced_structures = modifier.displace(ph_displ, etas, frac_coords=False)
# Generate the different shifts to average
ndiv = 2
shift1D = np.arange(1,2*ndiv+1,2)/(2*ndiv)
all_shifts = [[x,y,z] for x in shift1D for y in shift1D for z in shift1D]
all_shifts = [[0, 0, 0]]
for structure, eta in zip(displaced_structures, etas):
for shift in all_shifts:
flow.register_work(raman_work(structure, pseudos, shift))
return flow
def raman_work(structure, pseudos, shiftk, paral_kgb=1):
# Generate 3 different input files for computing optical properties with BSE.
# Global variables
global_vars = dict(
ecut=8,
istwfk="*1",
chksymbreak=0,
#nstep=4,
nstep=10,
paral_kgb=paral_kgb,
)
# GS run
scf_inp = abilab.AbinitInput(structure, pseudos=pseudos)
scf_inp.set_vars(global_vars)
scf_inp.set_kmesh(ngkpt=[2, 2, 2], shiftk=shiftk)
scf_inp["tolvrs"] = 1e-6
# NSCF run
nscf_inp = abilab.AbinitInput(structure, pseudos=pseudos)
nscf_inp.set_vars(global_vars)
nscf_inp.set_kmesh(ngkpt=[2, 2, 2], shiftk=shiftk)
nscf_inp.set_vars(
tolwfr=1e-8,
nband=12,
nbdbuf=4,
iscf=-2,
)
# BSE run with Model dielectric function and Haydock (only resonant + W + v)
# Note that SCR file is not needed here
bse_inp = abilab.AbinitInput(structure, pseudos=pseudos)
bse_inp.set_vars(global_vars)
bse_inp.set_kmesh(ngkpt=[2, 2, 2], shiftk=shiftk)
bse_inp.set_vars(
optdriver=99,
ecutwfn=global_vars["ecut"],
ecuteps=3,
inclvkb=2,
bs_algorithm=2, # Haydock
bs_haydock_niter=4, # No. of iterations for Haydock
bs_exchange_term=1,
bs_coulomb_term=21, # Use model W and full W_GG.
mdf_epsinf=12.0,
bs_calctype=1, # Use KS energies and orbitals to construct L0
mbpt_sciss="0.8 eV",
bs_coupling=0,
bs_loband=2,
nband=6,
#bs_freq_mesh="0 10 0.1 eV",
bs_hayd_term=0, # No terminator
)
# Build the work representing a BSE run with model dielectric function.
return flowtk.BseMdfWork(scf_inp, nscf_inp, bse_inp)
# This block generates the thumbnails in the AbiPy gallery.
# You can safely REMOVE this part if you are using this script for production runs.
if os.getenv("READTHEDOCS", False):
__name__ = None
import tempfile
options = flowtk.build_flow_main_parser().parse_args(["-w", tempfile.mkdtemp()])
build_flow(options).graphviz_imshow()
@flowtk.flow_main
def main(options):
"""
This is our main function that will be invoked by the script.
flow_main is a decorator implementing the command line interface.
Command line args are stored in `options`.
"""
return build_flow(options)
if __name__ == "__main__":
sys.exit(main())
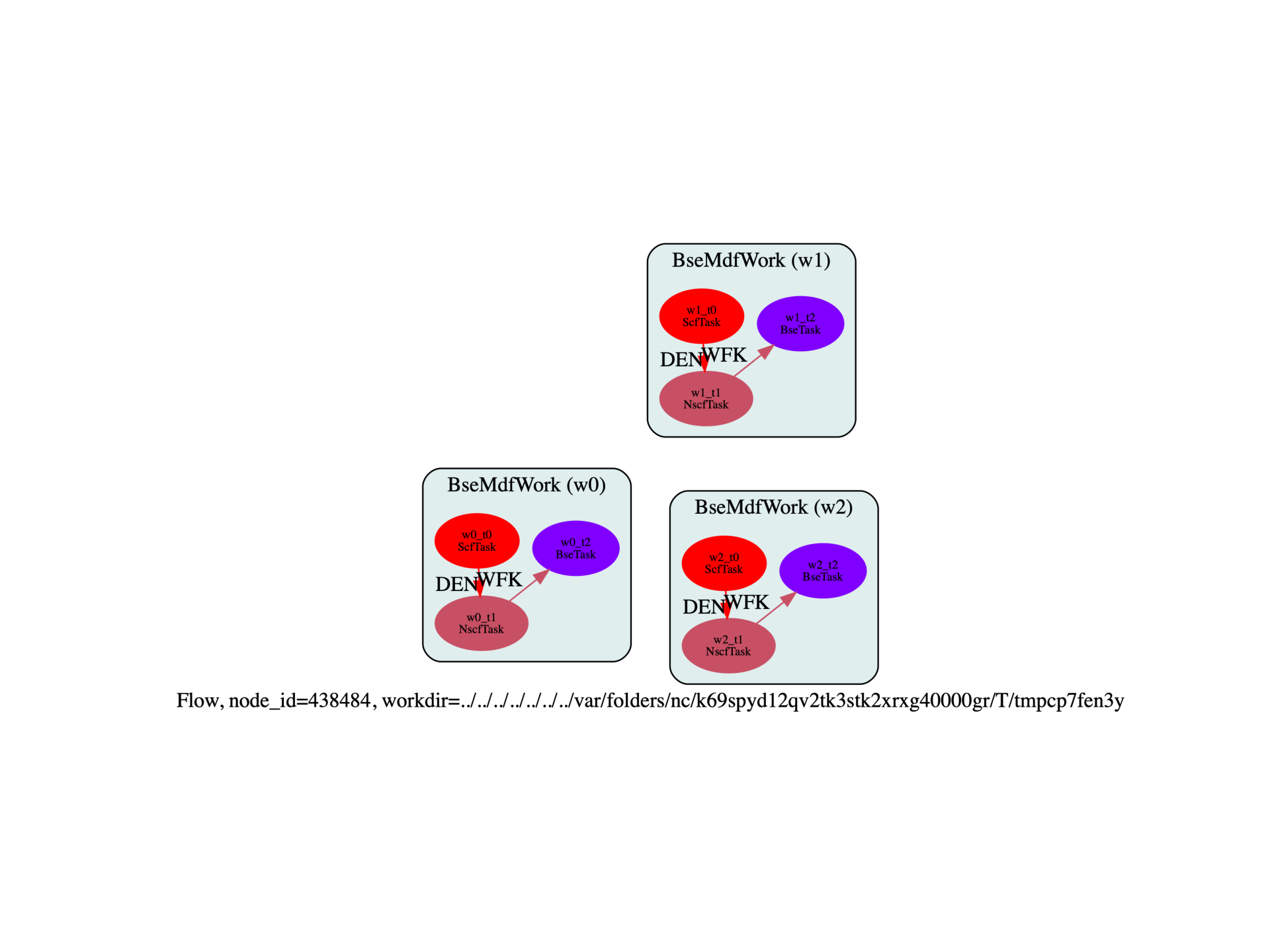
Run the script with:
run_raman_bse.py -s
then use:
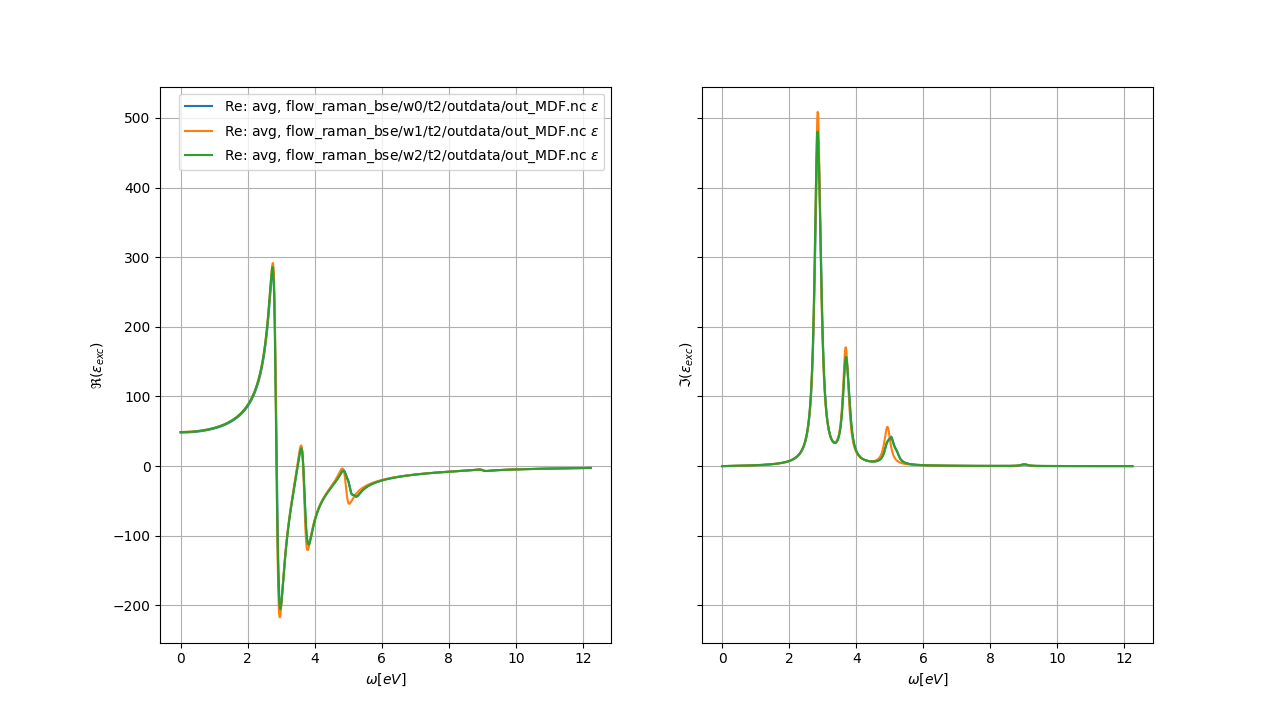
abirun.py flow_raman_bse robot MDF
to analyze all the macroscopic dielectric functions produced by the Flow with the robot. Inside the ipython terminal type:
[1] %matplotlib
[2] robot.plot()
to compare the real and imaginary part of the macroscopic dielectric function for the different displacements.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.540 seconds)