Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
G0W0 flow with convergence study wrt nband
This script shows how to compute the G0W0 corrections in silicon. More specifically, we build a flow to analyze the convergence of the QP corrections wrt to the number of bands in the self-energy. More complicated convergence studies can be implemented on the basis of this example.
import os
import sys
import abipy.data as data
import abipy.abilab as abilab
from abipy import flowtk
def make_inputs(ngkpt, paral_kgb=1):
# Crystalline silicon
# Calculation of the GW correction to the direct band gap in Gamma
# Dataset 1: ground state calculation
# Dataset 2: NSCF calculation
# Dataset 3: calculation of the screening
# Dataset 4-5-6: Self-Energy matrix elements (GW corrections) with different values of nband
multi = abilab.MultiDataset(structure=data.cif_file("si.cif"),
pseudos=data.pseudos("14si.pspnc"), ndtset=6)
# This grid is the most economical, but does not contain the Gamma point.
scf_kmesh = dict(
ngkpt=ngkpt,
shiftk=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5,
0.5, 0.0, 0.0,
0.0, 0.5, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.5]
)
# This grid contains the Gamma point, which is the point at which
# we will compute the (direct) band gap.
gw_kmesh = dict(
ngkpt=ngkpt,
shiftk=[0.0, 0.0, 0.0,
0.0, 0.5, 0.5,
0.5, 0.0, 0.5,
0.5, 0.5, 0.0]
)
# Global variables. gw_kmesh is used in all datasets except DATASET 1.
ecut = 6
multi.set_vars(
ecut=ecut,
timopt=-1,
istwfk="*1",
paral_kgb=paral_kgb,
gwpara=2,
)
multi.set_kmesh(**gw_kmesh)
# Dataset 1 (GS run)
multi[0].set_kmesh(**scf_kmesh)
multi[0].set_vars(
tolvrs=1e-6,
nband=4,
)
# Dataset 2 (NSCF run)
# Here we select the second dataset directly with the syntax multi[1]
multi[1].set_vars(
iscf=-2,
tolwfr=1e-12,
nband=35,
nbdbuf=5,
)
# Dataset3: Calculation of the screening.
multi[2].set_vars(
optdriver=3,
nband=25,
ecutwfn=ecut,
symchi=1,
inclvkb=0,
ecuteps=4.0,
ppmfrq="16.7 eV",
)
# Dataset4: Calculation of the Self-Energy matrix elements (GW corrections)
kptgw = [
-2.50000000E-01, -2.50000000E-01, 0.00000000E+00,
-2.50000000E-01, 2.50000000E-01, 0.00000000E+00,
5.00000000E-01, 5.00000000E-01, 0.00000000E+00,
-2.50000000E-01, 5.00000000E-01, 2.50000000E-01,
5.00000000E-01, 0.00000000E+00, 0.00000000E+00,
0.00000000E+00, 0.00000000E+00, 0.00000000E+00,
]
bdgw = [1, 8]
# Convergence study wrt nband in sigma.
for idx, nband in enumerate([10, 20, 30]):
multi[3+idx].set_vars(
optdriver=4,
nband=nband,
ecutwfn=ecut,
ecuteps=4.0,
ecutsigx=6.0,
symsigma=1,
#gw_qprange=0,
#nkptgw=0,
)
multi[3+idx].set_kptgw(kptgw, bdgw)
return multi.split_datasets()
def build_flow(options):
# Working directory (default is the name of the script with '.py' removed and "run_" replaced by "flow_")
if not options.workdir:
options.workdir = os.path.basename(sys.argv[0]).replace(".py", "").replace("run_","flow_")
# Change the value of ngkpt below to perform a GW calculation with a different k-mesh.
scf, nscf, scr, sig1, sig2, sig3 = make_inputs(ngkpt=[2, 2, 2])
return flowtk.g0w0_flow(options.workdir, scf, nscf, scr, [sig1, sig2, sig3], manager=options.manager)
# This block generates the thumbnails in the AbiPy gallery.
# You can safely REMOVE this part if you are using this script for production runs.
if os.getenv("READTHEDOCS", False):
__name__ = None
import tempfile
options = flowtk.build_flow_main_parser().parse_args(["-w", tempfile.mkdtemp()])
build_flow(options).graphviz_imshow()
@flowtk.flow_main
def main(options):
return build_flow(options)
if __name__ == "__main__":
sys.exit(main())
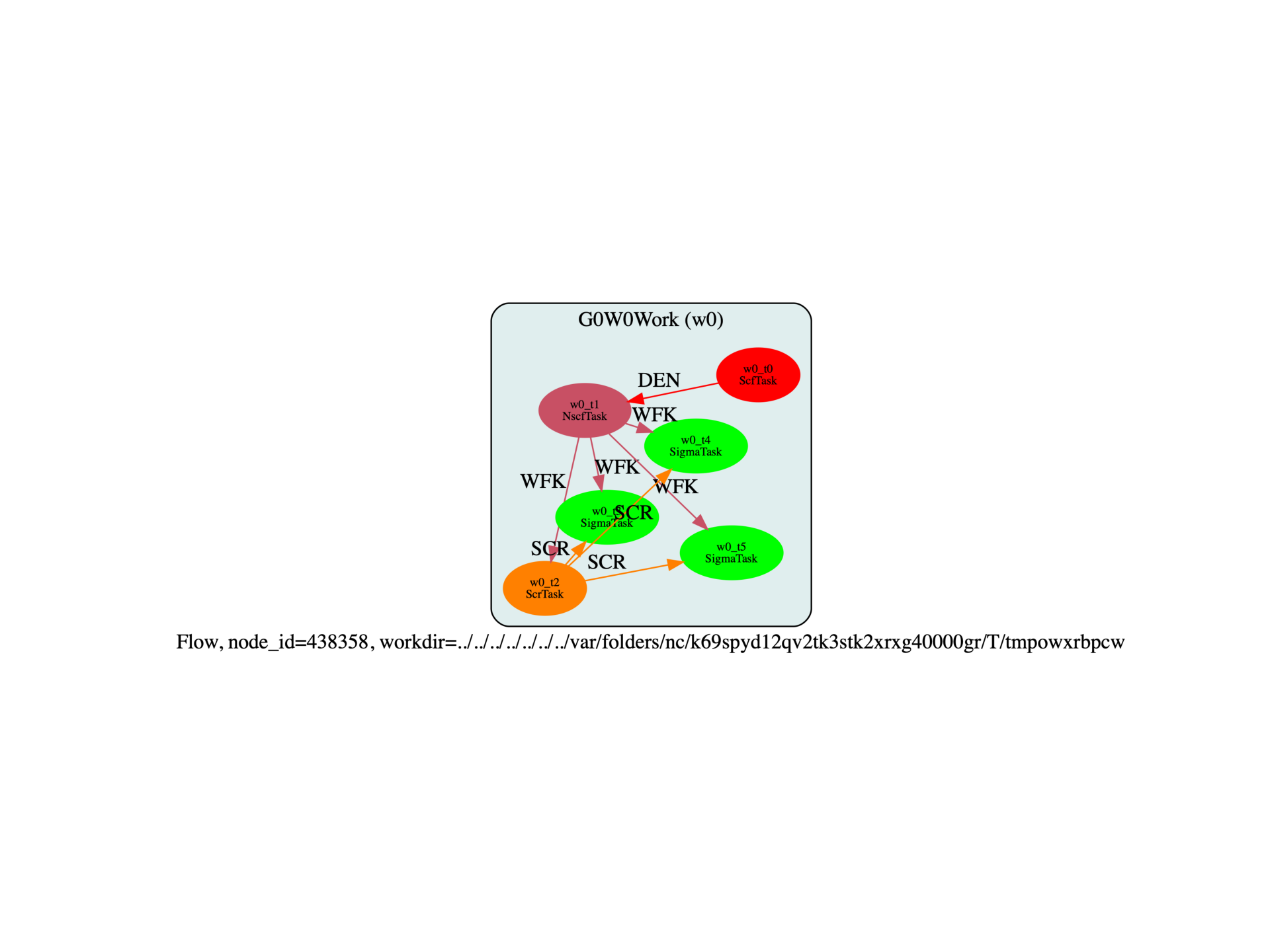
Run the script with:
run_si_g0w0.py -s
The last three tasks (w0_t3, w0_t4, w0_t5) are the SigmaTask who have produced
a netcdf file with the GW results with different number of bands.
We can check this with the command:
abirun.py flow_si_g0w0/ listext SIGRES
Found 3 files with extension `SIGRES` produced by the flow
File Size [Mb] Node_ID Node Class
---------------------------------------- ----------- --------- ------------
flow_si_g0w0/w0/t3/outdata/out_SIGRES.nc 0.05 241325 SigmaTask
flow_si_g0w0/w0/t4/outdata/out_SIGRES.nc 0.08 241326 SigmaTask
flow_si_g0w0/w0/t5/outdata/out_SIGRES.nc 0.13 241327 SigmaTask
Let’s use the SIGRES robot to collect and analyze the results:
abirun.py flow_si_g0w0/ robot SIGRES
and then, inside the ipython terminal, type:
In [1]: df = robot.get_dataframe()
In [2]: df
Out[2]:
nsppol qpgap ecutwfn \
flow_si_g0w0/w0/t3/outdata/out_SIGRES.nc 1 3.627960 5.914381651684836
flow_si_g0w0/w0/t4/outdata/out_SIGRES.nc 1 3.531781 5.914381651684836
flow_si_g0w0/w0/t5/outdata/out_SIGRES.nc 1 3.512285 5.914381651684836
ecuteps \
flow_si_g0w0/w0/t3/outdata/out_SIGRES.nc 3.6964885323070074
flow_si_g0w0/w0/t4/outdata/out_SIGRES.nc 3.6964885323070074
flow_si_g0w0/w0/t5/outdata/out_SIGRES.nc 3.6964885323070074
ecutsigx scr_nband \
flow_si_g0w0/w0/t3/outdata/out_SIGRES.nc 5.914381651684846 25
flow_si_g0w0/w0/t4/outdata/out_SIGRES.nc 5.914381651684846 25
flow_si_g0w0/w0/t5/outdata/out_SIGRES.nc 5.914381651684846 25
sigma_nband gwcalctyp scissor_ene \
flow_si_g0w0/w0/t3/outdata/out_SIGRES.nc 10 0 0.0
flow_si_g0w0/w0/t4/outdata/out_SIGRES.nc 20 0 0.0
flow_si_g0w0/w0/t5/outdata/out_SIGRES.nc 30 0 0.0
nkibz
flow_si_g0w0/w0/t3/outdata/out_SIGRES.nc 6
flow_si_g0w0/w0/t4/outdata/out_SIGRES.nc 6
flow_si_g0w0/w0/t5/outdata/out_SIGRES.nc 6
In [3]: %matplotlib
In [4]: df.plot("sigma_nband", "qpgap", marker="o")

Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.441 seconds)