Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Function1D object
This example shows how to use the Function1D object to analyze and plot results.
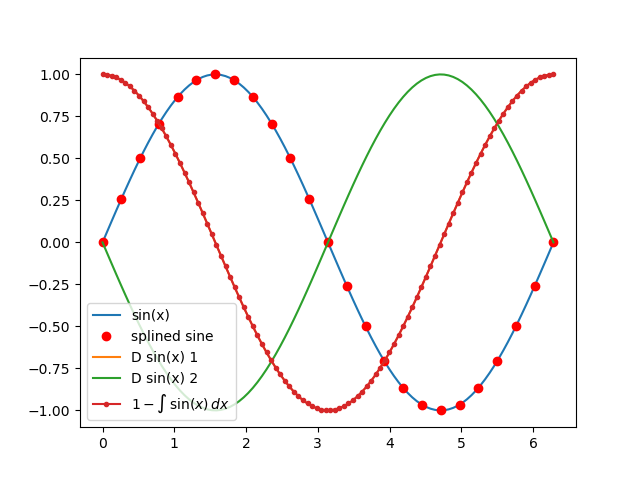
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from abipy.abilab import Function1D
# Build mesh [0, 2pi] with 100 points.
mesh = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, num=100)
# Compute sine function.
sine = Function1D.from_func(np.sin, mesh)
# Call matplotlib to plot data.
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
# Plot sine.
sine.plot_ax(ax, label="sin(x)")
# Spline sine on the coarse mesh sx, and plot the data.
sx = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, num=25)
splsine = sine.spline(sx)
plt.plot(sx, splsine, "ro", label="splined sine")
# Compute the 1-st and 2-nd order derivatives
# with finite differences (5-point stencil).
for order in [1,2]:
der = sine.finite_diff(order=order)
der.plot_ax(ax, label="D sin(x) %d" % order)
# Integrate the sine function and plot the results.
(1 - sine.integral()).plot_ax(ax, marker=".", label=r"$1 - \int\,\sin(x)\,dx$")
plt.legend(loc="best")
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.071 seconds)